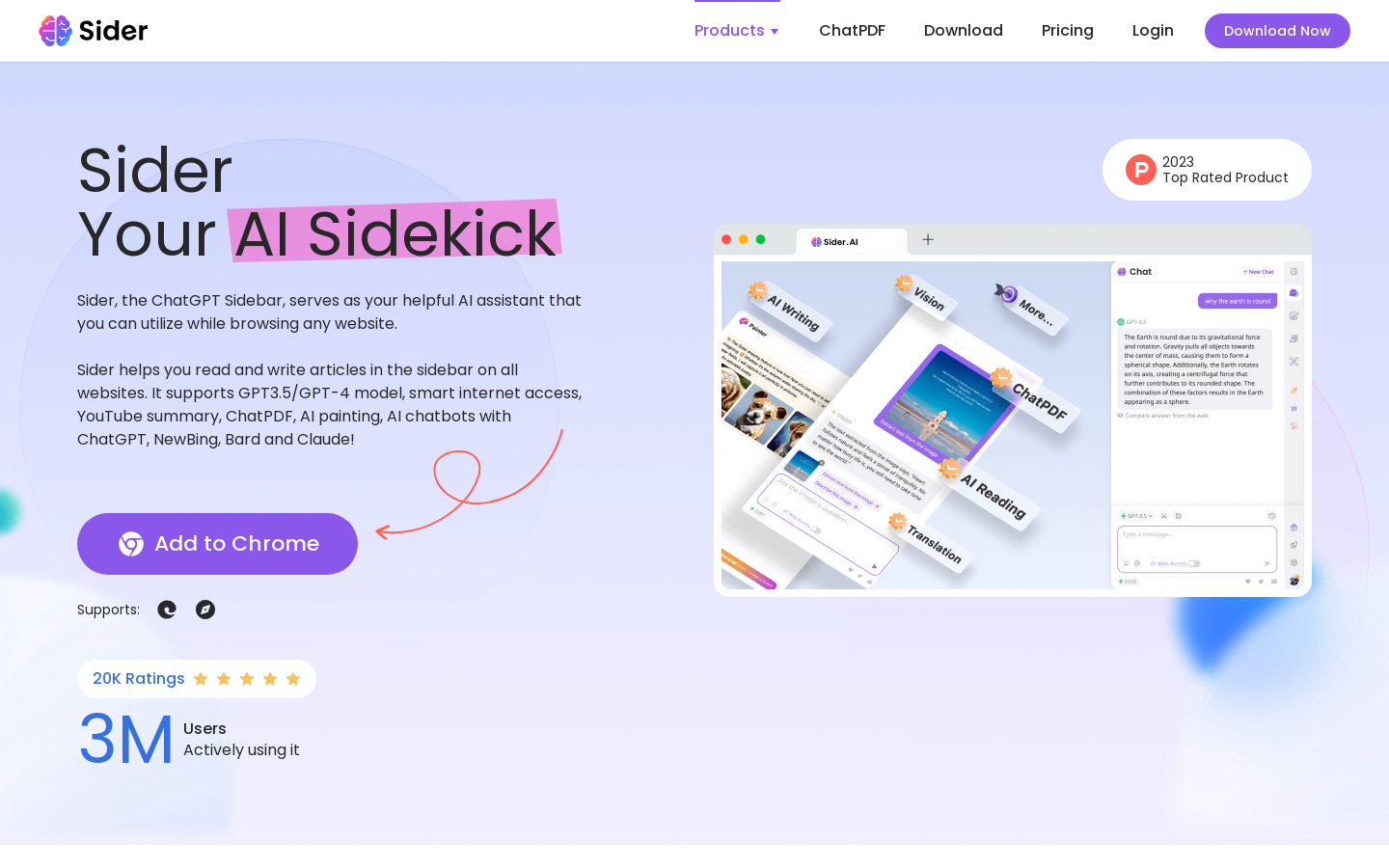
Sure! Quantum computing is a type of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to process and store information. In classical computers, information is represented using bits, which can be either a 0 or a 1. However, in quantum computers, information is stored in quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states at the same time.
One of the key concepts in quantum computing is superposition. This means that a qubit can be in a combination of 0 and 1 states simultaneously. It's like having a qubit that is both 0 and 1 at the same time. This allows quantum computers to perform many calculations simultaneously, which can lead to much faster processing speeds for certain types of problems.
Another important concept is entanglement. When qubits are entangled, the state of one qubit becomes connected to the state of another qubit, regardless of the distance between them. This means that changing the state of one qubit will instantly affect the state of the other qubit, even if they are far apart. Entanglement enables quantum computers to perform complex computations and solve certain problems more efficiently.
Quantum computing has the potential to solve problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. It could have applications in areas such as cryptography, optimization, drug discovery, and simulations. However, building practical quantum computers is still a significant challenge, and researchers are actively working on overcoming technical obstacles to make quantum computing a reality.
In summary, quantum computing is a new type of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to process and store information in qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously. It has the potential to revolutionize various fields by solving complex problems more efficiently.